- India will assume the Presidency of the G20 for one year from December 1, 2022 to November 30, 2023 and host next year’s G20 Leaders’ Summit in New Delhi.
- Mata Amritanandamayi Devi said that poverty in rural areas is one of the key issues to address in terms of moving ahead as a society overall.
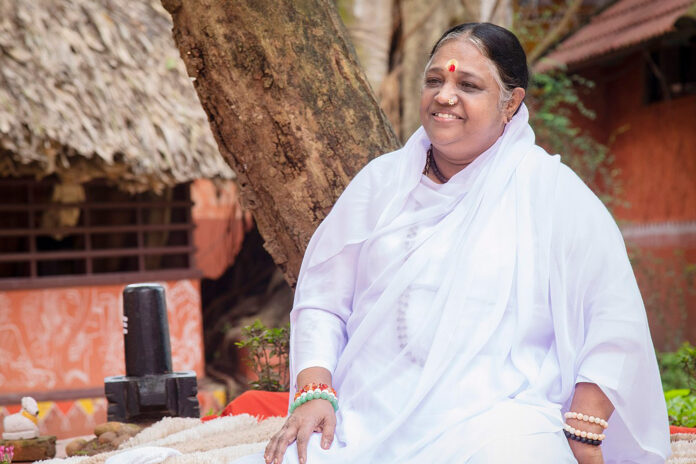
Kollam,Kerala /October 25th 2022: The Govt of India has appointed Mata Amritanandamayi Devi (Amma) as the Chair of the country’s Civil 20 (C20), an official engagement group of the Group of 20 (G20). The G20 is the premier intergovernmental forum for the world’s developed and emerging economies to address financial stability on a global basis. The C20 is its platform for civil-society organizations (CSOs) to bring forth non-government and non-business voices to the G20 leaders.
India will assume the Presidency of the G20 for one year from December 1, 2022 to November 30, 2023. The pinnacle of events is September 9-10, 2023 when the G20 Leaders’ Summit will take place in New Delhi at the level of Heads of State and Government. But in advance, India will host more than 200 meetings across the country, an endeavour that involves intense work by ministerial meetings, working groups, and engagement groups.
Upon accepting her role as Chair of India’s C20 engagement group, Amma expressed she was grateful to the Indian Government for arranging such a high-level representation of the voices of the common people. In addition, members include Sri M, the Satsang Foundation as Participant; Sudha Murthy, Chair, Infosys Foundation as Participant; Rambhau Mhalgi Prabodhini as Secretariat; and the Vivekananda Kendra, Kanyakumari as an Institutional Partner.
In the initial C20 online meeting Amma said: “Hunger, conflict, extinction of species, and environmental destruction are the most important issues facing the world today. We should put in sincere effort to develop solutions. If scientists of all fields—computer science, mathematics, physics, engineers, etc—would all work together, then we would be able to create more innovative methods of predicting environmental catastrophes, and thereby we would be able to save so many lives. Often, we see a lack of multidisciplinary and integrated effort. This is the need of the hour.”
She explained that poverty in rural areas is a key issue to address in terms of moving ahead as a society overall, especially since it is the people there who grow most of our food. Amma has been studying the lives of people in villages all over India and the world for more than 35 years. She has experienced that when we superficially look at villages from on high, we will not find holistic solutions. We need to go to the ground level and understand the issues from their point of view.
Amma said: “One of the fundamental causes of conflict is hunger. The issue of hunger is very complex. When we go into impoverished villages, we see that often the addictions of men lead to poverty. This poverty in turn prevents women from getting proper nutrition during the vital stages of pregnancy. As a result of malnourishment or even of absorbing toxins from contaminated food, their children die at birth. People need to be made aware of the need for nourishing women, especially pregnant women.”
She also spoke about the need to educate villagers about adopting practices outside their traditional ways, as in this day and age many of them are no longer sustainable. Sometimes existing infrastructures even lead to high-risk illnesses. In 2013, the Mata Amritanandamayi Math initiated Amrita SeRVe to help foster self-reliance in 108 impoverished villages throughout India.
“In the villages, we started a project called Jivamritam. Through this project, we provide clean drinking water and educate people on the importance of clean water. But there were people in some of the villages who blindly believed that they would only stay healthy by consuming the river water, which was polluted. They even believed that if they took the filtered water, they would develop kidney stones and bone diseases. So, in spite of being provided with clean, filtered water they continued to only drink the river water. As such, they continued to have various waterborne diseases,” said Amma.
“Everything needs balance. Just taking antidiabetic medications alone will not lower our blood sugar as long as we continue consuming sugar. So, we need to bring about awareness in the villages, but we also need to go into the villages ourselves and understand all the subtle and individual issues pertaining to each area.”
The G20 priorities for India include inclusive, equitable and sustainable growth; environmental sustainability; women’s empowerment; digital public infrastructure and tech-enabled development in areas ranging from health, agriculture and education to commerce, skill-mapping, culture and tourism; climate financing; circular economy; global food security; energy security; green hydrogen; disaster-risk reduction and resilience; developmental cooperation; fight against economic crime; and multilateral reforms.
Amma added: “All the issues raised here are vitally important. However, this should go beyond a mere physical meeting and become a true meeting—a meeting of hearts and minds. This is the only way to awaken ourselves and others.”
Also Read: Intelligent Minds Trusts’ Excellence in Education Awards 2022
The G20’s members consist of 19 countries plus the European Union, and India has been a member since its inception in 1999. Overall, the G20 accounts for about 80% of gross world product (GWP), 59-77% of international trade, two-thirds of the world’s population, and roughly half of its land area.
Under the auspices of the G20, C20 engages more than 800 civil societies, representatives, and networks of various countries, including organisations from countries who are not G20 members, to ensure that people of all strata of society are heard at the G20 Leaders’ Summit. Representation of CSOs among G20 member nations began in 2010 and was launched as an official G20 engagement group in 2013.
In addition to G20 Members, there has been a tradition of the G20 Presidency to invite guest countries and International Organizations (IOs) to its G20 meetings and Summit. Accordingly, in addition to regular International Organizations (UN, IMF, World Bank, WHO, WTO, ILO, FSB and OECD) and Chairs of Regional Organizations (AU, AUDA-NEPAD and ASEAN), India will be inviting Bangladesh, Egypt, Mauritius, Netherlands, Nigeria, Oman, Singapore, Spain and UAE as guest countries, as well as ISA (International Solar Alliance), CDRI (Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure) and ADB (Asian Development Bank) as Guest IOs.
This year’s G20 Leaders’ Summit is about to take place November 15-16 in Indonesia with the theme of “Recover Together Recover Strong.” Understanding the challenges and the need for collective action in the aftermath of COVID-19, Indonesia will focus on three main pillars for its Presidency: Global Health Architecture, Sustainable Energy Transition, and Digital Transformation.
About Mata Amritanandamayi Math
Amma’s organization exists to help alleviate the burden of the poor through helping to meet each of their five basic needs—food, shelter, healthcare, education, and livelihood—wherever and whenever possible. MAM is especially focused on meeting these needs in the aftermath of major disasters. To date, MAM has provided free medical care to more than 5.1 million people and subsidized care to another 300,000 patients—a total of ₹764 crore ($104 million US). It has also empowered 2.5 lakh women across India to earn a living through self-help groups (SHGs), built more than 47,000 houses for the homeless, provided financial aid for more than one lakh people unable to care for themselves, and given educational assistance to 50,000 children. Moreover, it is offering vocational-training, literacy training, running orphanages, hospices, old-age homes, scholarship programs, planting trees, and managing environmental-protection programs. MAM has done massive relief and rehabilitation work following the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, as well as in response to flooding in Mumbai, Gujarat, Chennai, Bihar, Uttarakhand and Jammu & Kashmir; earthquakes in Kashmir, Nepal, Haiti and Japan; cyclones in West Bengal and the Philippines; and hurricanes in the United States.
Visit EasyShiksha for skill development courses.