Researchers simulate in mice an acute decline in exercise, as many people experienced during Covid19 lockdowns, to study its metabolic consequences.
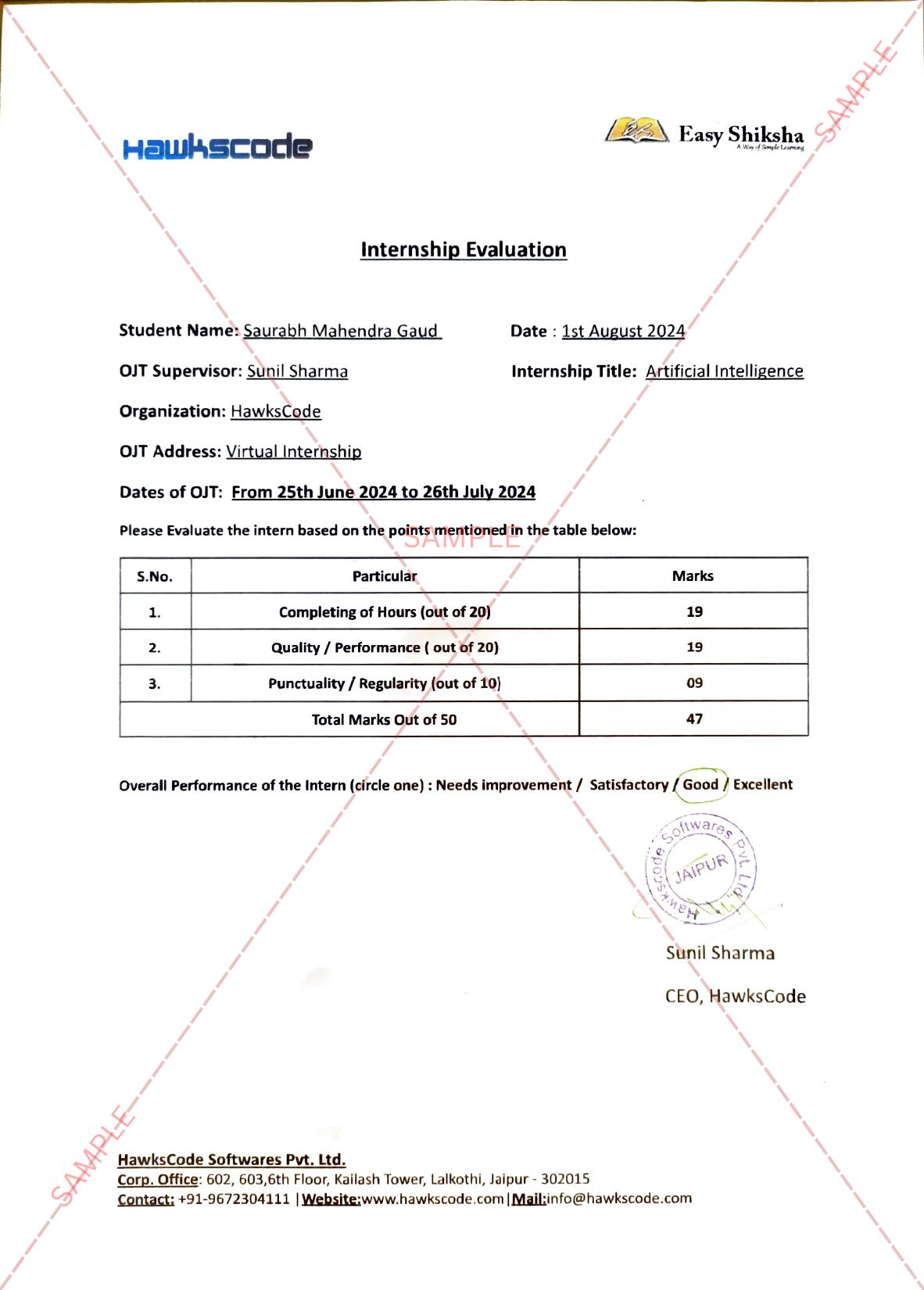
New Delhi, October 18th, 2021: Many people reported a sudden, sharp decline in exercise during COVID19 lockdowns, but few studies have examined its effect on metabolism and getting fat. The Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, National Institute for Biotechnology in the Negev, and Soroka University Medical Center researchers simulated in mice a sharp decline in physical activity by removing a voluntary running wheel and assessed how diet composition affects the response. They found that while less energy was spent by the mice, the mice still ate similar amounts of food as when the running wheel was present, which resulted in weight gain. Moreover, diet composition determined changes in the oxidation rates of fat or carbohydrates (sugars) – the two major energy sources of our body – in response to the decline in physical activity.

Important Announcement – EasyShiksha has now started Online Internship Program “Ab India Sikhega Ghar Se”
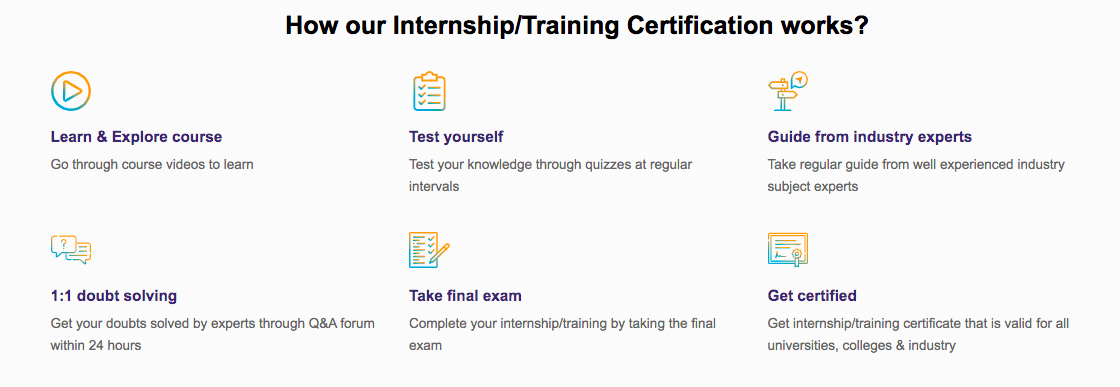
Q. Are EasyShiksha's internships truly free?
Yes, all internships offered by EasyShiksha are completely free of charge.
Q. How can I apply for an internship with EasyShiksha?
You can apply by visiting our website, browsing available internships, and following the application instructions provided.
Q. What types of internships are available through EasyShiksha?
EasyShiksha offers a wide range of internships across technology, business, marketing, healthcare, and more. Opportunities are continuously updated.
Q. Will I receive a certificate upon completing an internship?
Yes, upon successful completion, you will receive a certificate recognizing your participation and achievements.
Q. Are EasyShiksha's internship certificates recognized by universities and employers?
Yes, the certificates are recognized by universities, colleges, and employers worldwide.
Q. Is the download of certificates free or paid?
Access to internships and courses is free, but there is a small fee to download certificates, covering administrative costs.
Q. When can I start the course?
You can choose any course and start immediately without delay.
Q. What are the course and session timings?
These are fully online courses. You can learn at any time and pace. We recommend following a routine, but it depends on your schedule.
Q. What will happen when my course is over?
After completion, you will have lifetime access to the course for future reference.
Q. Can I download the notes and study material?
Yes, you can access and download course materials and have lifetime access for future reference.
Q. What software/tools would be needed for the course?
All necessary software/tools will be shared during the training as needed.
Q. I’m unable to make a payment. What should I do?
Try using a different card or account. If the problem persists, email us at info@easyshiksha.com.
Q. Do I get the certificate in hard copy?
No, only a soft copy is provided, which can be downloaded and printed if required.
Q. The payment got deducted but shows “failed”. What to do?
Technical errors may cause this. The deducted amount will be returned to your account in 7-10 working days.
Q. Payment was successful but dashboard shows ‘Buy Now’?
Sometimes payment reflection is delayed. If it takes longer than 30 minutes, email info@easyshiksha.com with the payment screenshot.
Q. What is the refund policy?
If you face technical issues, you can request a refund. No refunds are issued once the certificate has been generated.
Q. Can I enroll in a single course?
Yes, select the course of interest, fill in the details, make payment, and start learning. You will also earn a certificate.
Q. My questions are not listed above. I need further help.
Contact us at info@easyshiksha.com for further assistance.
Their findings were published in the peer-reviewed Physiological Reports, a journal of the American Physiological Society.
The mice were divided into two groups: one was fed a low-fat (=high carbohydrate) diet and the other a high-fat diet for six days. Mice were placed in metabolic cages, which measure their activity, food consumption, the amount of oxygen they consume and carbon dioxide (CO2) they release (from which carbohydrate and fat oxidation can be assessed). During the first 3 days, mice had access to a voluntary running wheel. The mice in both groups used it extensively during their active (nighttime) cycle. After three days, the running wheel was removed. Over those next three days, exercise dropped by 50%.
Prof. Assaf Rudich, Dr. Uri Yoel, and their group members, Dr. Yulia Haim, Dr. Nikhil S. Bhandarkar, and Ms. Rotem Lahav, discovered that the diet determined how much fat or carbohydrates were burned. With the running wheel in the cage, high-fat diet mice burned mainly fat throughout the day, and carbohydrate burning decreased, even more, when their physical activity dropped. The reverse was true for the low-fat (high carbohydrate) mice, who consumed during their wake hours more carbohydrates and decreased burning fat even further when the running wheel was taken out of the cage.
“Our findings show that there are immediate effects of exercise stoppage. While the comparison to human beings forced to become more sedentary during lockdowns requires confirmation in human clinical trials, our study provides a possible explanation as to how lockdowns may have induced weight gain. While the decline in spending energy is rapid, matching the lower energetic needs with lower food consumption takes time, resulting in a positive energy balance”, says Prof. Rudich.
Empower your team. Lead the industry
Get a subscription to a library of online courses and digital learning tools for your organization with EasyShiksha
Request NowDr. Uri Yoel, a clinical endocrinologist, adds: “Dietary composition determined the adaptation to less physical activity – the “rarer” energy source in the diet was the one that the mice chose to burn less of once the energy demand decreased. If also true in humans – this may have consequences on metabolism that need to be taken into consideration, particularly in persons with impaired metabolic regulation, such as diabetes.”
Prof. Rudich is a member of the Department of Clinical Biochemistry and Pharmacology at the Faculty of Health Sciences and a member of the National Institute for Biotechnology in the Negev. Dr. Uri Yoel is a member of the Faculty of Health Sciences at Ben-Gurion University and the Endocrinology Unit at Soroka.
The study was supported by a U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation Grant (No. 2017027), to Prof. Assaf Rudich and G. William Wong, one of the co-authors, professor of Physiology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
About Ben-Gurion University of the Negev:
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) is the fastest growing research university in Israel. With 20,000 students, 4,000 staff and faculty members, and three campuses in Beer-Sheva, Sde Boker and Eilat, BGU is an agent of change, fulfilling the vision of David Ben-Gurion, Israel’s legendary first prime minister, who envisaged the future of Israel emerging from the Negev. The University is at the heart of Beer-Sheva’s transformation into an innovation district, where leading multinational corporations and start-ups eagerly leverage BGU’s expertise to generate innovative R&D.
BGU effects change, locally, regionally and internationally. With faculties in Engineering Sciences; Health Sciences; Natural Sciences; Humanities and Social Sciences; Business and Management; and Desert Studies, the University is a recognized national and global leader in many fields, actively encouraging multi-disciplinary collaborations with government and industry, and nurturing entrepreneurship and innovation in all its forms.
BGU is also a university with a conscience, active both on the frontiers of science and in the community. Over a third of our students participate in one of the world’s most developed community action programs.
For more related content visit Easyshiksha and Hawkscode
ALSO READ: lsac-to-administer-lsat-india-2022-in-january-and-may
Get Course: Psychology Online