Ø Workers report low levels of wellbeing, regardless of working in a hybrid or non-hybrid environment, leading to rising levels of burnout
Ø The ABCD recommendations to organisations to prevent burnout
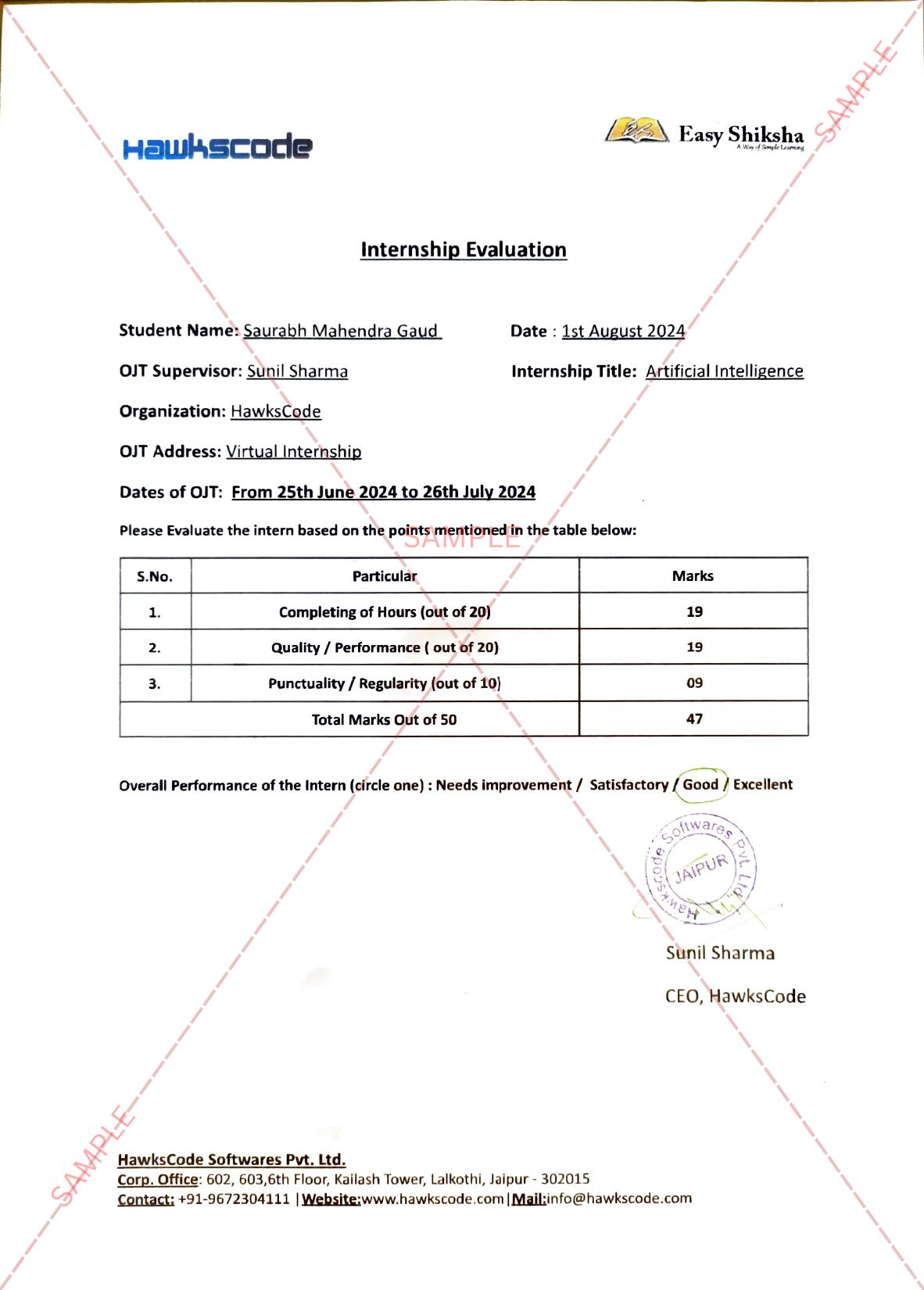
10 November 2022, Mumbai– It is beneficial for employers to provide greater flexibility and autonomy to their workforces, as 40% of workers report that they are experiencing burnout. That is according to research findings from the International SOS Foundation and Affinity Health at Work[1]. Affinity Health at Work is a specialist consultancy and one of the research groups contracted by the WHO Steering Group to perform the supporting evidence work for WHO guidelines on mental health at work, recently published in September 2022.
International SOS Foundation and Affinity Health at Work’s report Managing Duty of Care for Wellbeing Within a Hybrid Workforce, draws on data from workers across the world to investigate the impact of hybrid work on wellbeing and Duty of Care. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift towards hybrid working and brought about change in Duty of Care expectations and responsibilities over the last three years. Findings from Managing Duty of Care for Wellbeing Within a Hybrid Workforce show that on average, workers put in 20% more hours than they are expected to per week and that working hours are the most significant contributor to stress and mental ill-health. This could provide evidence for some of the reasons why the trend of ‘quiet quitting’ – when workers mentally disconnect from their jobs and start to only provide minimal effort – may be on the rise, as many workforce experts have noted.
Employers will be well placed to recognise the power of autonomy and flexibility, as the research indicates that these themes are often linked to greater mental wellbeing. The key issue for many workers is autonomy, as regardless of their working structure having a sense of control and power over their own work is often crucially important. Those employees who reported to have autonomy demonstrated a higher satisfaction overall with clearer responsibilities, better manager and colleague relationships and were more likely to disclose mental health issues with managers and colleagues.
Dr Rodrigo Rodriguez-Fernandez – Global Health Advisor, Wellness & Mental Health at International SOS, comments “Clearly workplace burnout is an issue that both hybrid and non-hybrid workers are experiencing. Both working environments come with their own challenges, which employers must account for in their mental wellness strategies. For instance, hybrid workers may experience wellbeing benefits associated with more work flexibility, but they may also miss out on in-person training for mental health awareness. Listening to employees is integral to this, as this research highlights how vital it is that employees feel empowered when it comes to their mental health and wellbeing.”
[1] An evidence-based-practice approach was taken to the research, using evidence from a number of sources – academic literature, practitioner literature, the local context, experts and those affected (in this case employees working a range of working patterns). Evidence from these three stages was then combined to develop the most accurate picture on which to base recommendations. 1,069 responses were received for the survey portion of the research. Results were analysed in order to gain further insights into the experience, needs and expectations of hybrid workers in terms of management of wellbeing.
Wellbeing as a Strategic Priority for Organisations
The extent of burnout and low levels of wellbeing in employees highlighted by the research demonstrates the importance of supporting mental health and wellbeing as a strategic priority for organisations. When creating solutions within organisations to support this strategic priority it is beneficial for organisations to gain an understanding of their employees’ needs and expectations. These then can be addressed through offering a range of tailored solutions for employees to support their wellbeing regardless of whether they are working in hybrid or non-hybrid environments. The research shows that just implementing training or a wellbeing hotline may not be enough. Organisations need a range of offerings to support employee wellbeing whilst also considering global differences in how useful different activities were perceived to be by workers. Offering a range of options of support means that the workers’ needs are acknowledged, which will in turn will increase the perceived level of fairness within the organisation. This approach can help combat the Great Resignation, maintain productivity levels, and protect the mental resilience of employees.
Rachel Lewis PhD – Registered Occupational Psychologist, Director at Affinity Health at Work, comments, “Duty of Care responsibilities are now more important than ever. Organisations need to, not only account for a variety of needs, but also offer additional support over and above a flexible working pattern. They should look for third party support when it comes to creating these solutions, as the input of external experts can often be vital, helping organisations to take a step-back and properly understand their employees’ needs. This support can include training, mental health assessments and short-term counselling, which more than ¾ of those surveyed found useful in supporting their mental health and wellbeing. When it comes to mental health and wellbeing, prevention is key. Investing in programmes to prevent mental ill health is going to provide the biggest return on investment. However, it is important to note that overall flexibility was most highly rated by all employees in comparison to any other type of support.”
ABCD Recommendations for Organisations to Counter Burnout and Low Levels of Wellbeing:
1. ADAPT to support the health and wellbeing of all employees as a strategic priority. A wellbeing programme is likely to involve providing a range of resources to build awareness and management of stress, and support for those who are struggling. However, this research shows that the key to realising positive wellbeing involves focusing on preventative approaches to build a healthy work environment.
2. BUILD solutions to address working hours and workload. Working hours and workload were found to be an issue for employees globally. It may be useful to set up a strategic working group to focus on solutions as well as cascading to working groups at a more local level. Solutions that have been shown to be beneficial to reducing working hours and workload include:
o the instigation of ‘recovery breaks’ where the whole organisation closes for a period of time (this could be an annual or bi-annual event for a month, or a decision about meeting-free afternoons each week)
o streamlining of processes to remove unnecessary repetition,
o and allowing greater autonomy within teams to allocate workload and prioritise actions.
3. CREATE an environment where time is taken to understand employee needs and expectations before actioning practices and processes. This research shows that different workers (by working pattern, individual differences and by continent) are likely to prioritise different practices and support offerings. Whilst it might be unrealistic to create bespoke arrangements for all individuals, organisations should take time to look at the profile of their workers. Options should then be offered that are likely to cater to the majority of employees, this will help acknowledge individual differences and increase the level of perceived fairness. Wherever possible, organisations should allow employees the opportunity to choose a working pattern that best suits the role they perform and their personal circumstances – taking account of what works for the organisation, what works for the team and what works for the individual. Through offering flexibility in this negotiation, organisations are likely to benefit from increased engagement and satisfaction.
Also Read: G20 provides a great opportunity for lending a healing touch to the world
4. DEVELOP a system to closely monitor the satisfaction of employees who are unable to choose hybrid working. Direct feedback from employees should be taken into account when making decisions regarding working patterns. Particularly with focus on feedback from women, as a difference in experience and perceived inequity has been highlighted by this research. Monitoring and ongoing analysis of results can both help counter the possible effects of the disconnect between senior leaders and other employees when considering hybrid working and can result in a strong consideration of relevant geographical differences.
Visit EasyShiksha for skill development courses