Photonic microwave generation using on-chip optical frequency combs
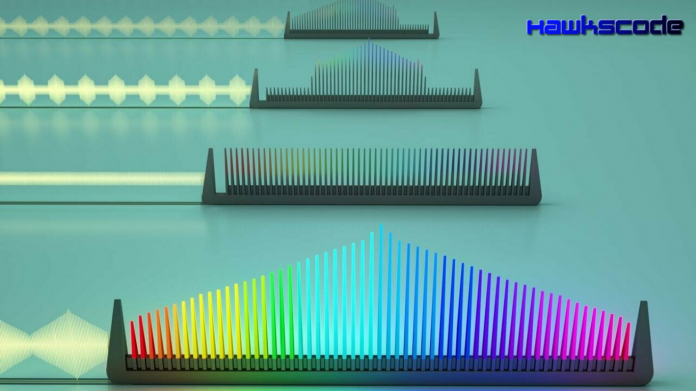
Photonic microwave generation using on-chip optical frequency.In our information society, the synthesis, distribution, and processing of radio and microwave signals are ubiquitous in wireless networks, telecommunications, and radars. A key building block of microwave photonics is optical frequency combs, which provide hundreds of equidistant and mutually coherent laser lines. They are ultrashort optical pulses emitted with a stable repetition rate that corresponds precisely to the frequency spacing of comb lines. The photodetection of the pulses produces a microwave carrier. To learn more tech things visist Easyshiksha.

Important Announcement – EasyShiksha has now started Online Internship Program “Ab India Sikhega Ghar Se”
In recent years there has been significant progress on chip-scale frequency combs generated from nonlinear microresonators driven by continuous-wave lasers. These frequency combs rely on the formation of dissipative Kerr solitons, which are ultrashort coherent light pulses circulating inside optical microresonators. Because of this,it is called ‘soliton microcombs.’
Publishing in Nature Photonics, an EPFL research team led by Tobias J. Kippenberg has now demonstrated integrated soliton microcombs with repetition rates as low as 10 GHz. This was achieved by significantly lowering the optical losses of integrated photonic waveguides based on silicon nitride.
Top Software Engineering Courses
Silicon nitride, Si3N4, is an excellent material for many CMOS applications, but it raises the threshold power level to create solitons. This effect keeps the repetition rate of soliton frequency combs too high to form signals in the X-band (around 10 GHz) and the K-band (roughly 20 GHz). The only way to get the repetition rate down to microwave levels was to use air cladding.
A low-noise continuous-wave fiber laser operating at 193 THz generated the solitons entering the photonic chip, creating combs with more than 300 frequency lines within a bandwidth of 3 dB.
I hope you like this blog, Photonic microwave generation using on-chip optical frequency. You can also learn about Quantum Computer Chips.
Empower your team. Lead the industry
Get a subscription to a library of online courses and digital learning tools for your organization with EasyShiksha
Request Now
ALSO READ: digite-infotech-donates-to-the-govt-of-indias-covid-19-relief
Get Course: Learn-SQL-Tutorial-for-Beginners